How to Upload My Jisam Data to Couchbase
In this tutorial, I volition show you lot how to upload/store images in MongoDB using Node.js & Express with the aid of multer & multer-gridfs-storage.
Related Posts:
– How to upload multiple files in Node.js
– Upload & resize multiple images in Node.js using Express, Multer, Sharp
– Node.js Express File Upload Residuum API (static folder) case using Multer
– Google Cloud Storage with Node.js: File Upload example
More than Practise:
– Node.js, Limited & MongoDb: Build a Grime Rest Api case
– Node.js + MongoDB: User Authentication & Authorization with JWT
Deployment: Docker Etch: Node.js Express and MongoDB instance
Contents
- Overview
- Node.js upload/store epitome in MongoDB
- Project Structure
- Setup Node.js modules
- Create View for uploading image
- Configure MongoDB database
- Create middleware for uploading & storing epitome
- Create Controller for the view
- Create Controller for uploading Images
- Define routes
- Create Express app server
- Run & Check outcome
- Node.js upload/shop multiple images in MongoDB
- Change form for uploading multiple images
- Modify middleware for uploading & storing epitome
- Controller for uploading multiple images
- Run & Check consequence
- Conclusion
- Farther Reading
- Source Code
Overview
Our Node.js Application will provide APIs for:
- uploading Files/Images to MongoDB
- getting list of Files' information (file proper noun & url)
- downloading File/Prototype from server with the url
This is the UI:

You tin can use an HTTP Customer for epitome upload:
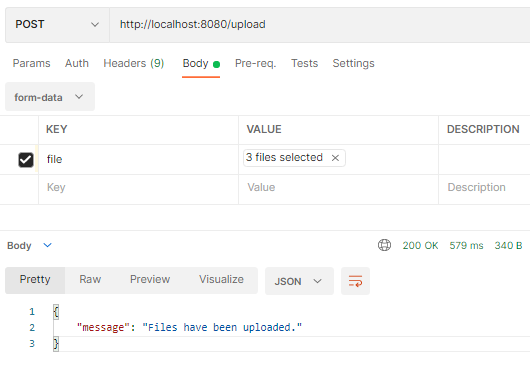
The images will be stored in two collections: photo.files and photos.chunks.
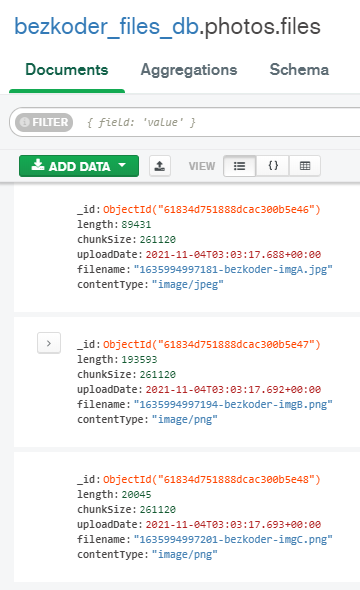
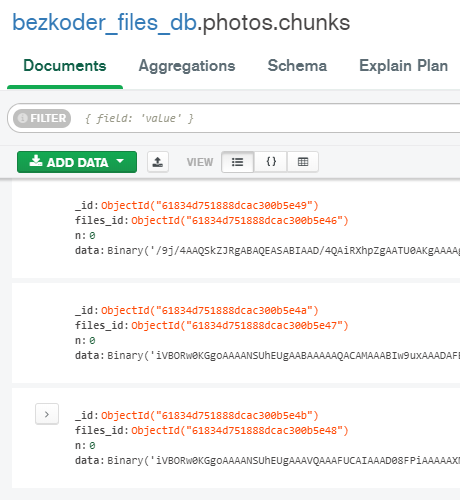
If we get listing of epitome files, the Node.js Rest Apis will return:
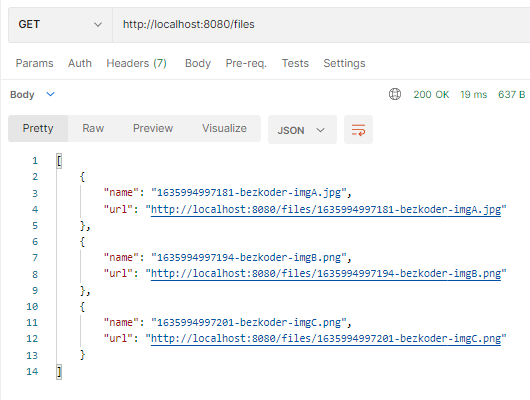
Each item in the response array has a url that yous can apply for downloading the file/image.
These are APIs to be exported:
| Methods | Urls | Actions |
|---|---|---|
| POST | /upload | upload a File/Image |
| GET | /files | get Listing of Images (name & url) |
| GET | /files/[filename] | download a File |
This Node.js App works with:
– Athwart 8 Client / Angular 10 Client / Angular 11 Client / Angular 12
– Angular Cloth 12
– Vue Client / Vuetify Client
– React Client / React Hooks Client
– Fabric UI Customer
– Axios Customer
Node.js upload/shop image in MongoDB
We're gonna prove you how to build this Node.js app step by footstep.
Project Structure
At present wait at our project construction:
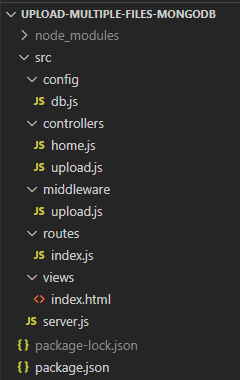
– config/db.js: includes configuration for MongoDB and Multer (url, database, image Bucket).
– views/alphabetize.html: contains HTML course for user to upload images.
– routes/index.js: defines routes for endpoints that is chosen from views, use controllers to handle requests.
– controllers:
-
dwelling.jsreturnsviews/index.html -
upload.jshandles upload, shop, display and download images
– middleware/upload.js: initializes Multer GridFs Storage engine (including MongoDB) and defines middleware part.
– server.js: initializes routes, configure CORS, runs Express app.
Setup Node.js modules
Open command prompt, modify electric current directory to the root folder of our project.
Install Express, CORS, Multer, Multer GridFs Storage and MongoDB with the following command:
npm install express cors multer multer-gridfs-storage mongodb The package.json file will look like this:
{ "name": "upload-multiple-images-mongodb", "version": "i.0.0", "clarification": "Node.js upload multiple files/images to MongoDB Demo", "master": "src/server.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no exam specified\" && get out one" }, "keywords": [ "node", "upload", "multiple", "files", "images", "mongodb" ], "writer": "bezkoder", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "cors": "^2.8.v", "express": "^4.17.1", "mongodb": "^4.1.3", "multer": "^1.4.3", "multer-gridfs-storage": "^5.0.ii" } } Create View for uploading paradigm
In views folder, create index.html file with the HTML and Javascript code as below:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-eight" /> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Uniform" content="ie=edge" /> <championship>Node.js upload images</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" /> <style> div.preview-images > img { width: 30%; } </manner> </caput> <torso> <div class="container"> <div course="row"> <div class="col-sm-8 mt-3"> <h4>Node.js upload images - bezkoder.com</h4> <form form="mt-4" action="/upload" method="Post" enctype="multipart/class-data" > <div class="form-grouping"> <input type="file" name="file" id="input-files" form="form-control-file border" /> </div> <button type="submit" grade="btn btn-primary">Submit</push button> </form> </div> </div> <hr /> <div course="row"> <div form="col-sm-12"> <div form="preview-images"></div> </div> </div> </div> <script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.one/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-three.4.1.min.js"></script> <script> $(certificate).set(function() { let imagesPreview = function(input, placeToInsertImagePreview) { if (input.files) { allow filesAmount = input.files.length; for (i = 0; i < filesAmount; i++) { let reader = new FileReader(); reader.onload = function(result) { $($.parseHTML("<img>")) .attr("src", event.target.result) .appendTo(placeToInsertImagePreview); }; reader.readAsDataURL(input.files[i]); } } }; $("#input-files").on("modify", function() { imagesPreview(this, "div.preview-images"); }); }); </script> </body> </html> For HTML part, we create a form with following elements:
-
activeness="/upload" -
method="Post" -
enctype="multipart/form-data"
Yous also need to detect the input tag with the name="file" aspect that nosotros will utilise in the middleware.
The jQuery script shows preview of the chosen images.
Nosotros also apply Bootstrap to make the UI more than comfortable to read.
Configure MongoDB database
config/db.js
module.exports = { url: "mongodb://localhost:27017/", database: "bezkoder_files_db", imgBucket: "photos", }; Create middleware for uploading & storing prototype
Inside middleware folder, create upload.js file with the following code:
const util = crave("util"); const multer = require("multer"); const { GridFsStorage } = crave("multer-gridfs-storage"); const dbConfig = require("../config/db"); var storage = new GridFsStorage({ url: dbConfig.url + dbConfig.database, options: { useNewUrlParser: truthful, useUnifiedTopology: truthful }, file: (req, file) => { const friction match = ["paradigm/png", "image/jpeg"]; if (match.indexOf(file.mimetype) === -1) { const filename = `${Date.now()}-bezkoder-${file.originalname}`; render filename; } return { bucketName: dbConfig.imgBucket, filename: `${Appointment.now()}-bezkoder-${file.originalname}` }; } }); var uploadFiles = multer({ storage: storage }).single("file"); var uploadFilesMiddleware = util.promisify(uploadFiles); module.exports = uploadFilesMiddleware; – We ascertain a storage configuration object with GridFsStorage grade.
-
url: must be a standard MongoDB connection string pointing to the MongoDB database.multer-gridfs-storagemodule will create a mongodb connection for you automatically. -
options: customizes how to institute the connection, specified in the MongoClient.connect documentation. -
file: this is the function to control the file storage in the database. The render value of this part is an object with the properties such as:filename,metadata,chunkSize,bucketName,contentType… We also check if the file is an image or not usingfile.mimetype. Then nosotros add the[timestamp]-bezkoder-prefix to the file's original proper noun to make sure that the duplicates never occur in MongoDB collection.bucketNameindicates that the file volition exist stored atphotos.chunksandphotos.filescollections.
– Adjacent we use multer module to initialize middleware and util.promisify() to brand the exported middleware object can be used with async-expect.
– The unmarried() office with the parameter is the name of input tag (in html view: <input type="file" name="file">) will shop the unmarried file in req.file.
If you lot want to do more, for instance, resize the images, please visit this mail:
Upload & resize multiple images in Node.js using Express, Multer, Sharp
Create Controller for the view
controllers/home.js
const path = crave("path"); const home = (req, res) => { return res.sendFile(path.join(`${__dirname}/../views/index.html`)); }; module.exports = { getHome: dwelling }; Create Controller for uploading Images
– For File Upload method, nosotros will consign upload() function that:
- use middleware part for file upload
- catch Multer error (in middleware function)
- return response with bulletin
– For Image File Information and Download:
-
getListFiles(): read all files in MongoDB collectionphotos.files, render list of files' information (name, url) -
download(): receives file name as input parameter, open download Stream from mongodb built-inGridFSBucket, so response.write(chunk) API to transfer the file to the client.
controllers/upload.js
const upload = require("../middleware/upload"); const dbConfig = require("../config/db"); const MongoClient = require("mongodb").MongoClient; const GridFSBucket = require("mongodb").GridFSBucket; const url = dbConfig.url; const baseUrl = "http://localhost:8080/files/"; const mongoClient = new MongoClient(url); const uploadFiles = async (req, res) => { try { look upload(req, res); panel.log(req.file); if (req.file == undefined) { return res.send({ message: "You must select a file.", }); } return res.transport({ message: "File has been uploaded.", }); } grab (fault) { console.log(error); return res.ship({ message: "Error when trying upload image: ${error}", }); } }; const getListFiles = async (req, res) => { try { await mongoClient.connect(); const database = mongoClient.db(dbConfig.database); const images = database.collection(dbConfig.imgBucket + ".files"); const cursor = images.find({}); if ((wait cursor.count()) === 0) { return res.status(500).send({ message: "No files found!", }); } let fileInfos = []; await cursor.forEach((doctor) => { fileInfos.push button({ name: doc.filename, url: baseUrl + doctor.filename, }); }); return res.status(200).send(fileInfos); } catch (mistake) { return res.status(500).ship({ message: error.message, }); } }; const download = async (req, res) => { try { expect mongoClient.connect(); const database = mongoClient.db(dbConfig.database); const bucket = new GridFSBucket(database, { bucketName: dbConfig.imgBucket, }); let downloadStream = saucepan.openDownloadStreamByName(req.params.name); downloadStream.on("data", role (data) { return res.status(200).write(data); }); downloadStream.on("error", function (err) { render res.status(404).send({ bulletin: "Cannot download the Paradigm!" }); }); downloadStream.on("end", () => { return res.end(); }); } grab (error) { return res.status(500).send({ message: error.message, }); } }; module.exports = { uploadFiles, getListFiles, download, }; Ascertain routes
In routes folder, define routes in alphabetize.js with Express Router.
const express = require("express"); const router = express.Router(); const homeController = crave("../controllers/habitation"); const uploadController = require("../controllers/upload"); let routes = app => { router.get("/", homeController.getHome); router.post("/upload", uploadController.uploadFiles); router.get("/files", uploadController.getListFiles); router.get("/files/:name", uploadController.download); return app.use("/", router); }; module.exports = routes; There are four routes:
– GET: Dwelling page for the upload grade.
– POST "/upload" to call the uploadFiles function of the controller. This is as well for activity="/upload" in the view.
– Become /files for listing of Images.
– Become /files/:name to download the paradigm with the file proper noun.
Create Limited app server
Finally, we create an Express server.
server.js
const cors = require("cors"); const express = require("limited"); const app = express(); const initRoutes = require("./routes"); var corsOptions = { origin: "http://localhost:8081" }; app.use(cors(corsOptions)); app.utilise(limited.urlencoded({ extended: true })); initRoutes(app); let port = 8080; app.listen(port, () => { console.log(`Running at localhost:${port}`); }); What we do are:
– import express and cors modules:
- Limited is for edifice the Remainder apis
- cors provides Express middleware to enable CORS with diverse options.
– create an Express app, then add cors middlewares using app.utilise() method. Notice that we fix origin: http://localhost:8081.
– listen on port 8080 for incoming requests.
Run & Bank check result
On the project root folder, run this command: node src/server.js
The console shows:
Running at localhost:8080 Open browser with url http://localhost:8080/.
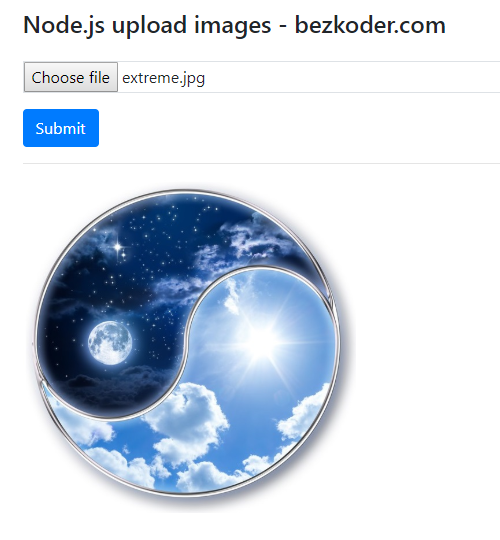
Click on Submit button, if the file is uploaded and stored in MongoDB successfully, the console shows image's information:
{ fieldname: 'file', originalname: 'farthermost.jpg', encoding: '7bit', mimetype: 'epitome/jpeg', id: 5dd60e6aee27a520ccad86a0, filename: '1574309482432-bezkoder-extreme.jpg', metadata: nothing, bucketName: 'photos', chunkSize: 261120, size: 89431, md5: '0d072efbb134b3b186c5da705e0e7059', uploadDate: 2019-11-21T04:11:23.264Z, contentType: 'image/jpeg' } Cheque MongoDB database, you volition run into bezkoder_files_db with two collections: photos.chunks & photo.files:

Node.js upload/store multiple images in MongoDB
At present I will show you how to modify some code to deal with multiple images instead of simply one image at a time.
Change form for uploading multiple images
For the form, we write the input tag with new multiple attribute like this.
views/index.html
<input type="file" proper noun="file" multiple id="input-files" class="course-command-file edge" /> Change middleware for uploading & storing image
For multiple images, we employ some other function: array() instead of unmarried().
middleware/upload.js
... // var uploadFile = multer({ storage: storage }).single("file"); var uploadFiles = multer({ storage: storage }).array("file", x); var uploadFilesMiddleware = util.promisify(uploadFiles); module.exports = uploadFilesMiddleware; – array() function limits the number of files to upload each fourth dimension, the first parameter is the proper noun of – input tag (in html view: <input type="file" proper noun="file">), the second parameter is the max number of files (x).
Controller for uploading multiple images
With the controller, nosotros update the uploadFiles office.
controllers/upload.js
const uploadFiles = async (req, res) => { try { await upload(req, res); panel.log(req.files); if (req.files.length <= 0) { return res .status(400) .send({ message: "You must select at least ane file." }); } return res.status(200).transport({ message: "Files have been uploaded.", }); // console.log(req.file); // if (req.file == undefined) { // return res.ship({ // message: "You must select a file.", // }); // } // return res.send({ // message: "File has been uploaded.", // }); } catch (mistake) { panel.log(error); if (error.code === "LIMIT_UNEXPECTED_FILE") { return res.status(400).transport({ message: "Too many files to upload.", }); } return res.status(500).send({ message: `Error when trying upload many files: ${fault}`, }); // return res.send({ // message: "Error when trying upload image: ${error}", // }); } }; There is a additional function in the grab() block. We bank check if the error.code is "LIMIT_UNEXPECTED_FILE" for showing user the message when he tries to upload more than than 10 images/files.
Don't forget to change the controller method on router:
router.post("/upload", uploadController.uploadFiles); Run & Bank check result
Run the command: node src/server.js
And the panel shows:
Running at localhost:8080 Open up your browser with url http://localhost:8080/, add together some images like this:
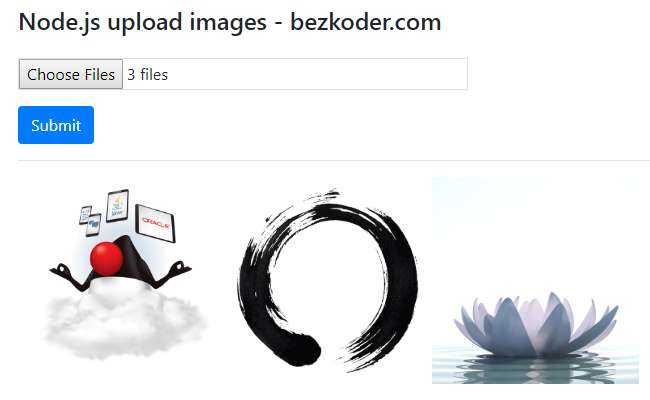
Click on Submit push. If these images are uploaded and stored in MongoDB successfully, you tin see:

The panel shows these images' data:
[ { fieldname: 'multi-files', originalname: 'circumvolve.png', encoding: '7bit', mimetype: 'image/png', id: 5dd637361ae0143fdc572105, filename: '1574319926050-bezkoder-circle.png', metadata: null, bucketName: 'photos', chunkSize: 261120, size: 193593, md5: 'f6455d94e5ec26a1b6eb75b334220cbd', uploadDate: 2019-11-21T07:05:30.273Z, contentType: 'prototype/png' }, { fieldname: 'multi-files', originalname: 'JavaDuke.png', encoding: '7bit', mimetype: 'image/png', id: 5dd637361ae0143fdc572106, filename: '1574319926110-bezkoder-JavaDuke.png', metadata: null, bucketName: 'photos', chunkSize: 261120, size: 112767, md5: 'b7f0fa8ea1932850d99a64b35484484a', uploadDate: 2019-xi-21T07:05:30.275Z, contentType: 'image/png' }, { fieldname: 'multi-files', originalname: 'lotus.jpg', encoding: '7bit', mimetype: 'image/jpeg', id: 5dd637361ae0143fdc572107, filename: '1574319926121-bezkoder-lotus.jpg', metadata: null, bucketName: 'photos', chunkSize: 261120, size: 375719, md5: '26dc2e512d7c021daaa7cb46215d4a5b', uploadDate: 2019-11-21T07:05:32.326Z, contentType: 'image/jpeg' } ] Check MongoDB database:
- photos.files drove:

- chunks.files collection:

If you endeavour to upload more than 10 files at a time, you tin see the error like this:

Conclusion
Today we've learned how to upload and store unmarried/multiple images in MongoDB database using express, multer & multer-gridfs-storage modules, way to limit the number of files by configuration.
We also know how to get list of uploaded files/images, and provide urls for download.
Happy learning! Come across you lot once more.
Further Reading
- https://world wide web.npmjs.com/bundle/express
- https://www.npmjs.com/package/cors
- https://www.npmjs.com/packet/multer
- https://www.npmjs.com/bundle/multer-gridfs-storage
- https://world wide web.npmjs.com/packet/mongodb
Node.js & MongoDB Associations:
- MongoDB One-to-One human relationship tutorial with Mongoose example
- MongoDB One-to-Many Relationship tutorial with Mongoose examples
- MongoDB Many-to-Many Relationship with Mongoose examples
Fullstack CRUD App:
- Athwart eight + Node.js Express + MongoDB
- Angular ten + Node.js Express + MongoDB
- Athwart xi + Node.js Limited + MongoDB
- Athwart 12 + Node.js Express + MongoDB
- React.js + Node.js Express + MongoDB
- Vue.js + Node.js Express + MongoDB
Deployment: Docker Etch: Node.js Limited and MongoDB example
Source Lawmaking
You tin can observe the complete source code for this tutorial at Github.
Source: https://www.bezkoder.com/node-js-upload-store-images-mongodb/
0 Response to "How to Upload My Jisam Data to Couchbase"
Post a Comment